If you’re reading this article, it means that your device is connected to a computer network. Networks like the one you’re connected to right now have transformed the way we communicate, access information, and work. But just like most everything in the world of technology, they can be taken advantage of by those who understand them. That’s why understand them yourself is one of the best ways to safeguard your security. The good news that while they can be extremely complex when examined up close, the basic concepts behind them are easy to understand. So here we go.
What Is a Computer Network?
Before we go any further, we need to first clarify what a computer network actually is. Here’s IBM’s definition of the term: A computer network comprises two or more computers that are connected—either by cables (wired) or Wi-Fi (wireless)—with the purpose of transmitting, exchanging, or sharing data and resources. (Source) The last part is especially important because it explains why connected computers are a lot more useful than computers that are isolated from one another. Here are some things that computer networks are used for:
- Sharing one printer between multiple computers.
- Accessing files stored in a centralized location.
- Communicating using text, audio, and video.
What Are the Main Types of Computer Networks?
Computer networks are like residential neighborhoods because they all have their own unique characteristics. We can broadly categorize them based on how the connections between individual computers are made into two main categories:
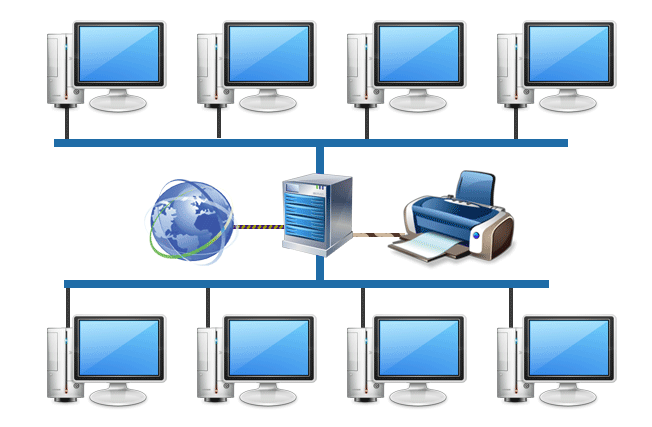
- Local Area Network (LAN): When several office computers are connected together using network cables or wireless (Wireless Local Area Network – WLAN) connections to share files, folders, printers, or scanners, they form what’s called a local area network (or LAN for short). These networks are formed in a connected location such as a home or business.
- Wide-Area Networks (WAN): This type of network connects computers or local area networks to other local area networks to work together as one network. If you think about a business with two office locations that need to share the same files or printers, they are typically connected through a WAN. On a grander scale, you are actually using the largest wide-area network (WAN) in the world right now by accessing the internet. Instead of only a few office locations, it’s connecting a vast collection of networks and gateways that link 22 billion devices and even more computer users across every continent.
Both local and wide area networks can be isolated from the rest of the world, or they can be connected to the internet. When a computer network is connected to the internet, it’s like when an animal is released into the wild after spending its entire life safely isolated from dangerous predators. Suddenly, the network can catch the attention of cybercriminals or become infected with malware, which is why network security is so important.
What Makes a Computer Network Work?
If you were to place several computers, printers, and fax machines next to one another and connect them all using network cables, you would quickly discover that it takes more than just connections for a computer network to operate as intended. That’s because computers are all about logic, so the networked devices have to be arranged in a specific way and follow clearly defined rules to share data and resources.
There are many different ways a computer network can be arranged, but the one arrangement (topology) you’re most likely to see in a small office with just a few computers is called a collapsed ring. This arrangement involves a central router to which all computers that constitute the network are connected to, either using a cable or wirelessly. As explained by Cisco, the router works as a dispatcher, directing traffic and choosing the most efficient route for information, in the form of data packets, to travel across a network. Routers also manage the information exchange between the local network and the internet, so it’s paramount to use one from a reputable manufacturer that cares about the security of its products. The data packets are nothing but bundles of data with the source address of the sending computer and the destination address of the receiving computer attached to them. Thanks to this system, we can exchange information with the office printer just as easily as we can with someone located on the other side of the world.
Stay Safe out There
As you’ve undoubtedly seen, you don’t need to be a networking expert to enjoy the benefits of computer networks. But understanding networks helps you identify where the possible weaknesses are that can allow hackers to attack. And as long as you partner with a capable MSP, you also don’t need to worry about the numerous threats that all public networks face. If you’re interested in finding out more about how we can keep your systems and networks safe while providing you with the most uptime possible, just reach out. It doesn’t take long to talk you through what it takes to make sure you’re as secure as you can be.